.net core 使用阿里云分布式日志的配置方法
前言
好久没有出来夸白了,今天教大家简单的使用阿里云分布式日志,来存储日志,没有阿里云账号的,可以免费注册一个

开通阿里云分布式日志(有一定的免费额度,个人测试学习完全没问题的,香)
阿里云日志地址:https://sls.console.aliyun.com/lognext/profile
先开通阿里云日志,这个比较简单授权就可以了
选择接入数据,我们这里选 .net

选择项目名称,没有项目的可以去创建一个,项目名称后面会用到,如果你有购买阿里云ecs,项目区域最好选择跟ecs同一个区域(每个区域的地址不一样,同一个区域可以选择内网通讯,速度更快),如果没有,就随便选个区域,我这里选择的是杭州
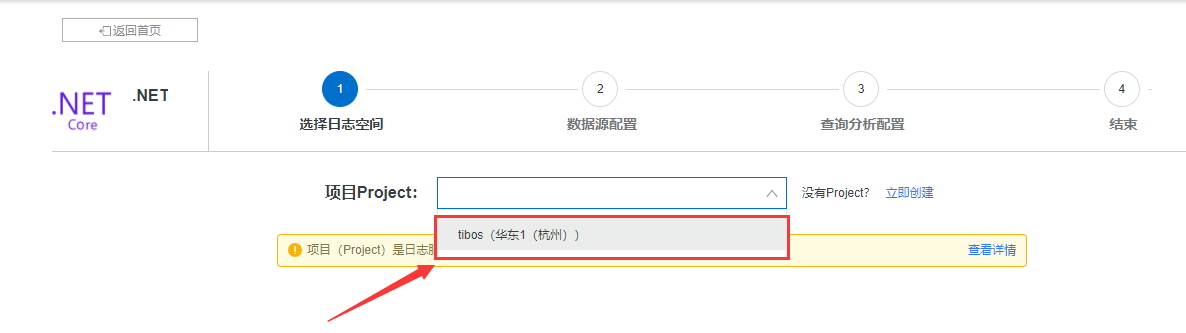
选择日志库,没有就创建一个
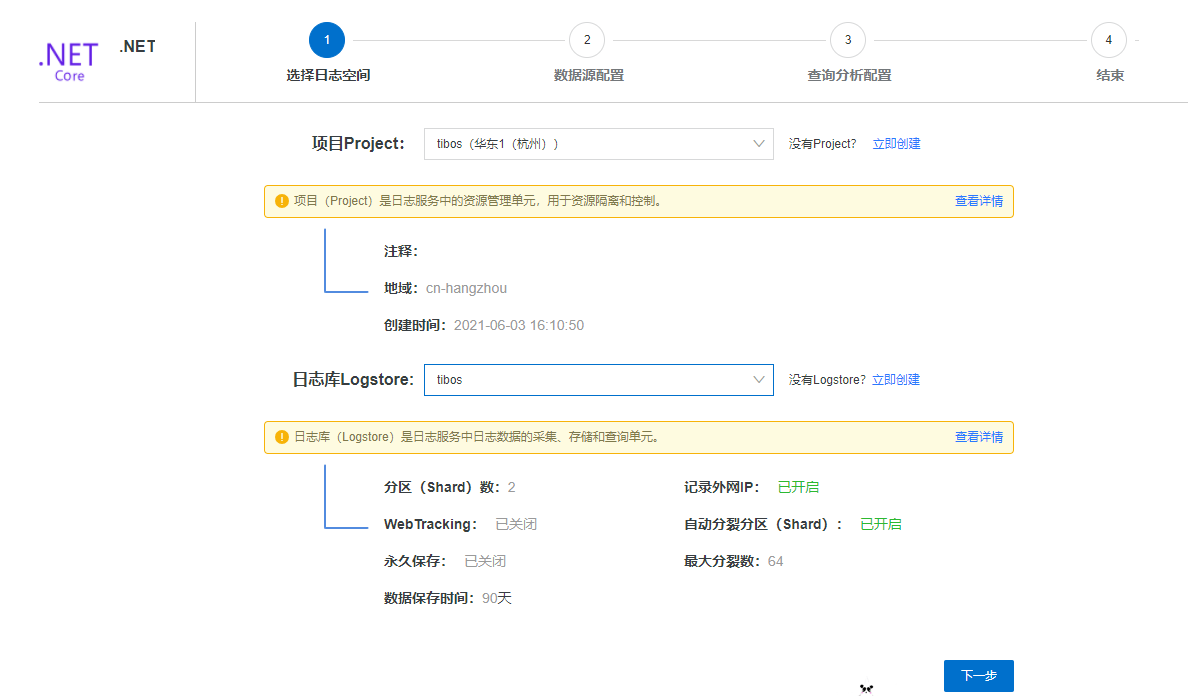
数据源配置,这个先不用管,后面有教程
设置分析配置,例如我这里设置了两个,可以根据业务需求来,没有特殊要求不用设置
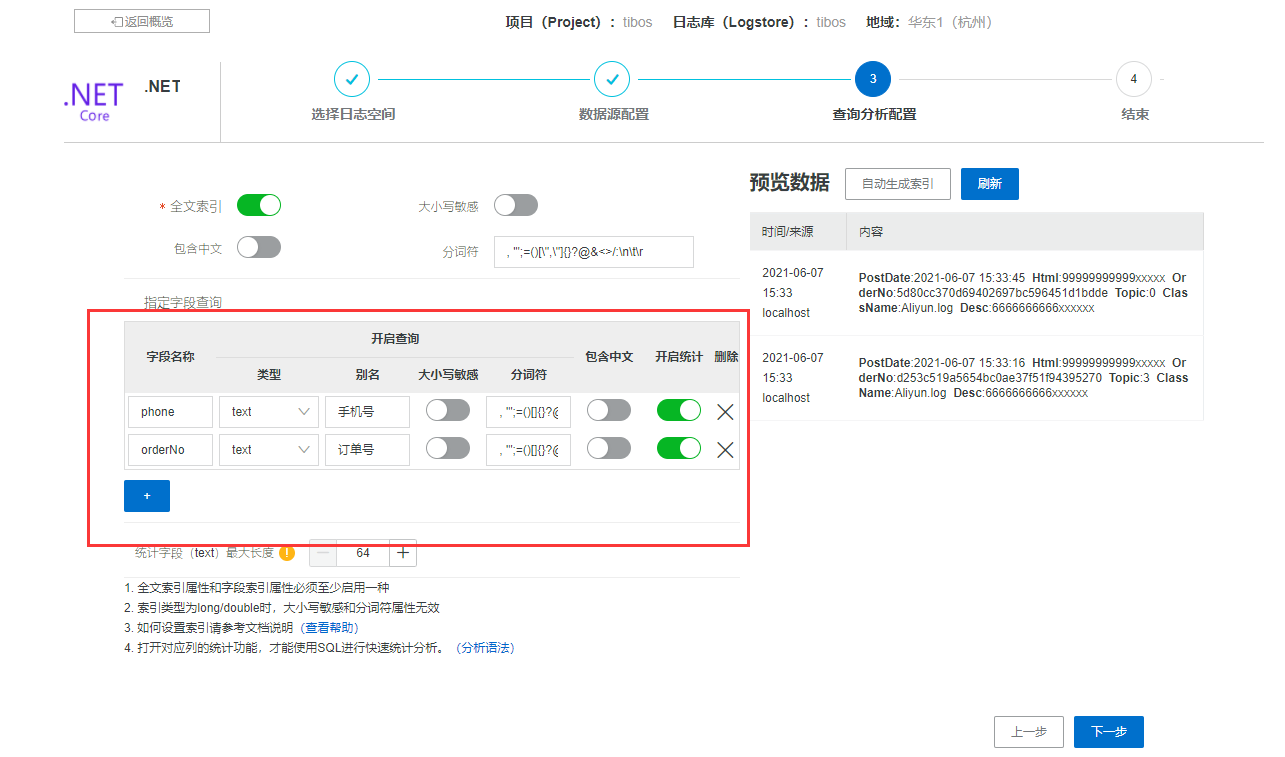
开通完成,可以正常看到仪盘表

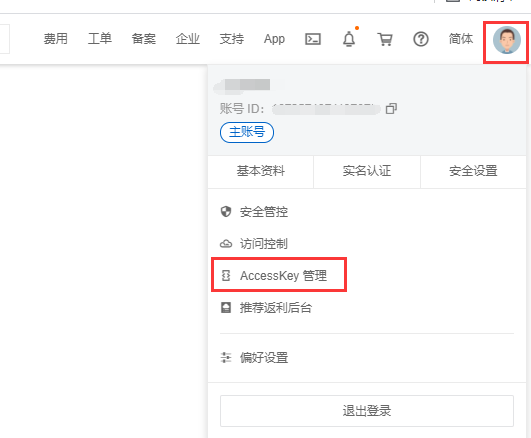
设置密钥
通过sdk 写入日志
阿里云有提供对应的sdk(阿里云 .net sdk的质量大家都懂),它主要是通过构造一个静态对象来提供访问的,地址: https://github.com/aliyun/aliyun-log-dotnetcore-sdk
阿里云代码
logserviceclientbuilders.httpbuilder
.endpoint("<endpoint>", "<projectname>")
.credential("<accesskeyid>", "<accesskey>")
.build();
阿里云提供的依赖注入代码(autofac),很遗憾按照这个方式,并没有获取到对象
using aliyun.api.logservice;
using autofac;
namespace examples.dependencyinjection
{
public static class autofacexample
{
public static void register(containerbuilder containerbuilder)
{
containerbuilder
.register(context => logserviceclientbuilders.httpbuilder
// 服务入口<endpoint>及项目名<projectname>
.endpoint("<endpoint>", "<projectname>")
// 访问密钥信息
.credential("<accesskeyid>", "<accesskey>")
.build())
// `ilogserviceclient`所有成员是线程安全的,建议使用singleton模式。
.singleinstance();
}
}
}
中间个有小插曲,由于公司使用阿里云日志比较早,也非常稳定,替换成我申请的阿里云日志的配置,发送日志一直报错,找了半天没找到原因,提了工单,原来阿里云使用了新的sdk



重新封装阿里云日志sdk(aliyun.log.core) https://github.com/wmowm/aliyun.log.core问了下群友,刚好有大佬重写过向阿里云提交日志这块,一番py交易,代码块到手,主要是数据组装,加密,发送,发送部分的代码基于http的protobuf服务实现,这里直接从阿里云开源的sdk里拷贝过来,开始重新封装,主要实现以下功能
- 实现.net core di
- 加入队列,让日志先入列,再提交到阿里云,提高系统吞吐量
- 对日志模型进行封装,满足基础业务需求
代码如下
添加servicecollection 拓展,定义一个阿里云日志的配置信息委托,然后将需要注入的服务注册进去即可
public static aliyunlogbuilder addaliyunlog(this iservicecollection services, action<aliyunslsoptions> setupaction)
{
if (setupaction == null)
{
throw new argumentnullexception(nameof(setupaction));
}
//var options = new aliyunslsoptions();
//setupaction(options);
services.configure(setupaction);
services.addhttpclient();
services.addsingleton<aliyunslsclient>();
services.addsingleton<aliyunlogclient>();
services.addhostedservice<hostedservice>();
return new aliyunlogbuilder(services);
}
加入队列比较简单,定义一个队列,使用hostedservice 消费队列
/// <summary>
/// 写日志
/// </summary>
/// <param name="log"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public async task log(logmodel log)
{
aliyunlogbuilder.logqueue.enqueue(log);
}
/// <summary>
/// 消费队列
/// </summary>
task.run(async () =>
{
using (var servicescope = _provider.getservice<iservicescopefactory>().createscope())
{
var _options = servicescope.serviceprovider.getrequiredservice<ioptions<aliyunslsoptions>>();
var _client = servicescope.serviceprovider.getrequiredservice<aliyunslsclient>();
while (true)
{
try
{
if (aliyunlogbuilder.logqueue.count>0)
{
var log = aliyunlogbuilder.logqueue.dequeue();
var loginfo = new loginfo
{
contents =
{
{"topic", log.topic.tostring()},
{"orderno", log.orderno},
{"classname", log.classname},
{ "desc",log.desc},
{ "html",log.html},
{ "postdate",log.postdate},
},
time = datetime.parse(log.postdate)
};
list<loginfo> list = new list<loginfo>() { loginfo };
var loggroupinfo = new loggroupinfo
{
topic = log.topic.tostring(),
source = "localhost",
logs = list
};
await _client.postlogs(new postlogsrequest(_options.value.logstorename, loggroupinfo));
}
else
{
await task.delay(1000);
}
}
catch (exception ex)
{
await task.delay(1000);
}
}
}
});
定义日志模型,可以根据业务情况拓展
public class logmodel
{
/// <summary>
/// 所在类
/// </summary>
public string classname { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 订单号
/// </summary>
public string orderno { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 提交时间
/// </summary>
public string postdate { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 描述
/// </summary>
public string desc { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 长字段描述
/// </summary>
public string html { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 日志主题
/// </summary>
public string topic { get; set; } = "3";
}
使用aliyun.log.core
获取aliyun.log.core包
方案a. install-package aliyun.log.core
方案b. nuget包管理工具搜索 aliyun.log.core
添加中间件
services.addaliyunlog(m =>
{
m.accesskey = sls.getvalue<string>("accesskey");
m.accesskeyid = sls.getvalue<string>("accesskeyid");
m.endpoint = sls.getvalue<string>("host");
m.project = sls.getvalue<string>("project");
m.logstorename = sls.getvalue<string>("logstorename");
});
写入日志
//获取对象
private readonly ioptions<slsoptions> _options;
private readonly aliyunlogclient _aliyunlogclient;
public homecontroller(ioptions<slsoptions> options, aliyunlogclient aliyunlogclient)
{
_options = options;
_aliyunlogclient = aliyunlogclient;
}
[httpget("/api/sendlog")]
public async task<jsonresult> sendlog(string topic="1")
{
//日志模型
logmodel logmodel = new logmodel()
{
classname = "aliyun.log",
desc = "6666666666xxxxxx",
html = "99999999999xxxxx",
topic = topic,
orderno = guid.newguid().tostring("n"),
postdate = datetime.now.tostring("yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss")
};
await _aliyunlogclient.log(logmodel);
return json("0");
}
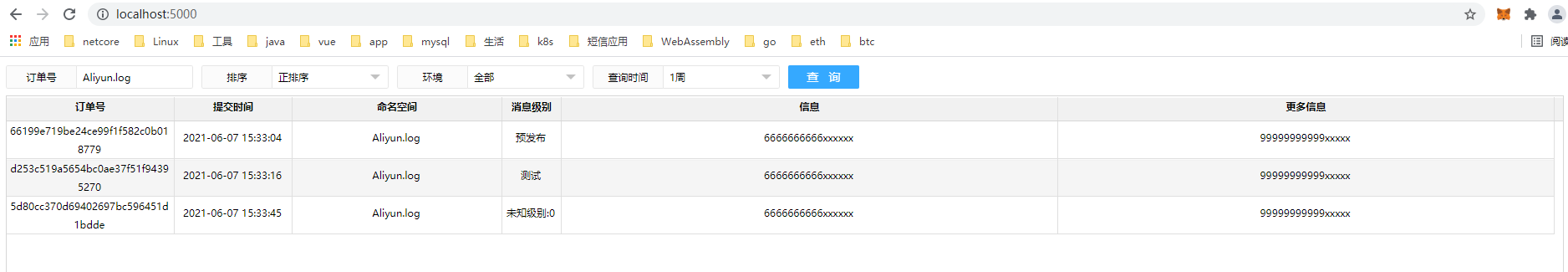
简单的查询日志
同事写了一个查询阿里云日志的工具,非常实用,我用 .net core又抄了一遍,一并开源在github,地址: https://github.com/wmowm/aliyun.log.core/tree/main/aliyun.log.core.client
推荐我自己写的一个redis消息队列中间件initq,操作简单可以下载的玩玩
https://github.com/wmowm/initq
关于.net core 使用阿里云分布式日志的文章就介绍至此,更多相关.net core分布式日志内容请搜索硕编程以前的文章,希望大家多多支持硕编程!




